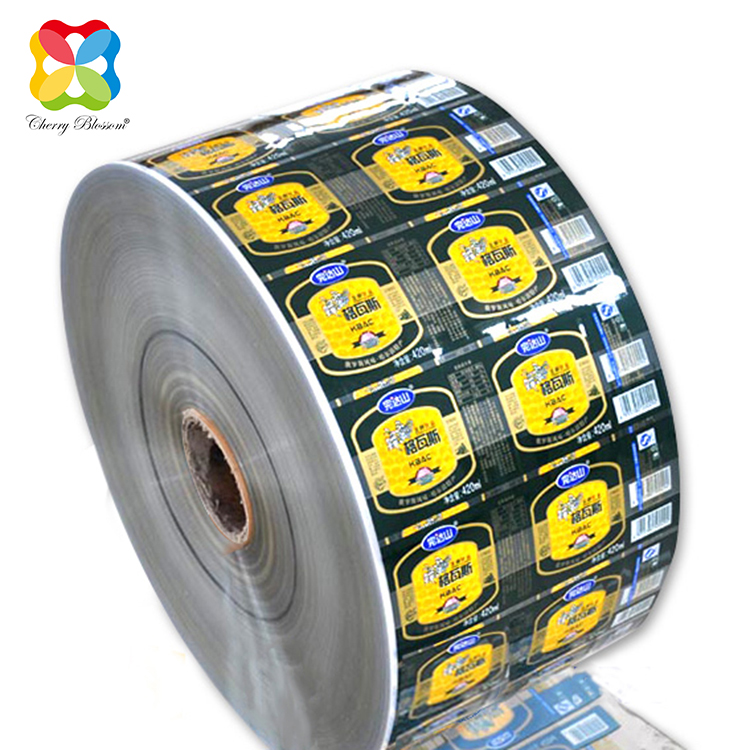
Heat shrink film labels are thin film labels printed on plastic films or tubes using specialized ink. During the labeling process, when heated (around 70 ℃), the shrink label quickly shrinks along the outer contour of the container and adheres tightly to the surface of the container. Heat shrink film labels mainly include shrink sleeve labels and shrink wrap labels.



Function characteristics
Shrinkage sleeve label is a cylindrical label made from heat shrink film as the substrate, which is printed and then made. It has the characteristic of convenient use and is extremely suitable for special-shaped containers. Shrink sleeve labels generally require specialized labeling equipment to cover the printed label onto the container. Firstly, the labeling device opens the sealed cylindrical sleeve label, which may sometimes require drilling; Next, cut the label into appropriate sizes and place it on the container; Then use steam, infrared, or hot air channels for heat treatment to tightly attach the label to the surface of the container.
Due to the high transparency of the film itself, the label has a bright and glossy color. However, due to the need for shrinkage during use, there is a drawback of pattern deformation, especially for products printed with barcode markings. Strict design and printing quality control must be carried out, otherwise the deformation of the pattern will cause the barcode quality to be unqualified. Shrink wrap labels can be labeled using traditional labeling equipment, which requires the use of adhesives and higher temperatures during the labeling process. During the shrinkage process, hot melt adhesive is preferred due to the stress generated by the adhesive at the overlapping parts of the film.



Prepress production
Due to the fact that heat shrink film is a thermoplastic film that is oriented by stretching during production and shrinks during use. Therefore, no matter which printing method is used for printing, before designing the surface pattern, the horizontal and vertical shrinkage rates of the material, as well as the allowable deformation errors in various directions of the decorative graphics and text after shrinkage, must be considered to ensure the accurate restoration of the pattern, text, and barcode shrunk onto the container.
The direction of the pattern
Whether the heat shrink film is printed using gravure printing or flexographic printing, its printing is mainly in the inner printing method, and the direction relative to the pattern on the printing plate should be positive. Nowadays, there are also shrink films for surface printing. In this case, the pattern direction on the printing plate should be reversed.
The hierarchy of patterns
Due to the limitations of flexographic printing, if the shrink film is printed using flexographic printing, the level of the image should not be too delicate, while using gravure printing can require a richer level of image.
Design of dimensions
The transverse shrinkage rate of the heat shrink film material used for printing is 50% to 52% and 60% to 62%, and can reach 90% under special circumstances. The longitudinal shrinkage rate is required to be 6% to 8%. However, during the instantaneous contraction of the film, due to the limitations of the container, the horizontal and vertical directions cannot be fully contracted. To ensure the accurate restoration of the contracted pattern, text, and barcode, it is necessary to consider the shape of the container and calculate the correct size and deformation rate based on the actual situation. For heat shrink labels that require converting sheet-like films into cylindrical shapes and sealing the overlapping areas together with adhesive, it is important to note that no graphics or text should be designed at the sealing areas to avoid affecting the bonding strength.
Barcode placement
Usually, the placement direction of the barcode should be consistent with the printing direction, otherwise it will cause distortion of the barcode lines, which will affect the scanning results and cause misreading. In addition, the color selection of label products should focus on spot colors as much as possible, and the production of white versions is necessary, which can be made into full or hollow according to the actual situation. The color of barcodes should follow the conventional requirements, that is, the color combination of bars and spaces should comply with the principle of barcode color matching. Selection of printing materials. The printing of heat shrink labels has been briefly analyzed, and besides controlling the printing process well, the material plays a decisive role in its quality. Therefore, selecting the appropriate materials is crucial. Determine the thickness of the film material based on the application field, cost, characteristics of the film, shrinkage performance, printing process, and labeling process requirements of the heat shrink label. The general requirement for making shrink film labels is that the thickness of the film should be between 30 microns and 70 microns, with 50 microns, 45 microns, and 40 microns being commonly used. The specific thickness depends on the labeling performance of the labeling equipment. For the selected label material, it is generally required that the shrinkage rate of the film material is within the application range, and the transverse (TD) shrinkage rate is higher than the longitudinal (MD) shrinkage rate. The lateral shrinkage rates of commonly used materials are 50% to 52% and 60% to 62%, and can reach 90% in special cases. The longitudinal shrinkage rate is required to be between 6% and 8%. In addition, due to the high sensitivity of the shrink film to heat, it is important to avoid high temperatures during storage, printing, and transportation.



Printing essentials
Unlike paper labels, heat shrink film uses non absorbent printing materials such as PVC, PP, PETG, OPS, OPP, and various multi-layer co extruded films. The properties of these materials determine that their printing process is different from paper labels. In traditional offset printing, flexographic printing (flexographic printing), gravure printing, and silk screen printing, the printing method of heat shrink film labels is still mainly gravure printing. The main reason is that there is a large number of domestic gravure printing machines, and the competition for printing costs is fierce. In addition, gravure printing products have the characteristics of thick ink layer, bright colors, and rich layers, and these types of labels are mainly long plate printing. The gravure printing can withstand millions of sheets, So for live parts with large printing capacity, it is undoubtedly the most cost-effective. However, with the intensification of market competition and the development of technologies such as flexographic plate making, machinery, and ink, the proportion of flexographic printing is increasing year by year. But from the customer's perspective, what matters more is meeting quality standards, reducing costs, and choosing the appropriate printing method.
Control of tension
Due to the fact that thin films are more susceptible to tension changes during the printing process, resulting in inaccurate registration, it is important to pay close attention to tension control during the printing process to maintain stability and balance of tension. The size of tension adjustment should be determined based on the type and tensile strength of the film. For example, if the tensile strength of the film is weak and prone to tensile deformation, the tension should be relatively small; For films with strong tensile strength, the tension can be correspondingly increased. In the case of a certain type of film, the width and thickness of the film are also important factors determining the magnitude of tension. Wide films should have a greater tension than narrow films, while thicker films have a greater tension than thinner films.
Gravure heat shrink film mainly uses unit type gravure printing machines, which are now equipped with tension automatic control systems and automatic color registration control systems. Based on the measured error between color registration marks, the tension in the uncoiling area, printing area, and winding area is automatically adjusted to ensure stable tension in the printing process and the accuracy of final printing. Compared with stacked and unit type flexographic printing machines, CI type flexographic printing machines are more suitable for using flexographic heat shrink films. This is because during the printing process, each color group shares a common imprinting drum, and the substrate material and imprinting drum are tightly attached, with small changes in tension, resulting in small tensile deformation of the material and high registration accuracy.
Ink selection
There are four main types of inks used for shrink film printing: solvent based inks, water-based inks, cationic UV inks, and free radical UV inks. In terms of application, solvent based inks dominate in the field of shrink film label printing, followed by water-based inks and free radical UV inks. However, cationic UV inks are not widely used in the shrink film field due to their high price and difficulty in printing. The solvent based ink is mainly used for heat shrink films in gravure and flexographic printing. Different films should use specialized ink and cannot be mixed. Ink companies generally provide three solvent ratios for ink corresponding to different materials: fast drying, medium drying, and slow drying. Printing factories can choose the appropriate solvent ratio based on actual production conditions such as workshop temperature and printing speed. In addition, water-based ink and UV ink can also be used. However, regardless of the type of ink used, it is necessary to fully consider that the performance indicators of the ink must meet the requirements. For example, the shrinkage rate of ink must match the shrinkage characteristics of the heat shrink film, otherwise it may cause the ink layer to split or even deink.
Control of drying temperature
It is very important to control the drying temperature well when printing heat shrink films. If the drying temperature is too high, the material will experience thermal shrinkage; If the temperature is too low, the ink will not dry thoroughly enough, resulting in final adhesion and dirt on the back. Color drying devices are installed on both gravure and flexographic printing machines to ensure complete drying of each color of ink. At the same time, in order to prevent deformation of the material during the drying process, it is required to set up cold air channels between the color decks to control the influence of residual heat. Nowadays, frozen drums are used in printing machines, which can quickly reduce the temperature of materials during the printing process. Due to the common printing suitability of shrink films, such as strong chemical stability, low surface energy, smooth surface without absorption, and poor affinity with printing ink. Therefore, regardless of the printing method used, the film needs to undergo surface corona discharge treatment to improve its surface energy and roughness, and improve the adhesion fastness of ink on the material surface.



Post time: Jan-25-2024